Nitrogen-based fertilisers
Nitrogen-based fertilisers are the most widely used fertilisers worldwide. However, nitrogen losses due to volatilisation, denitrification, and leaching impose significant annual costs on Australian farmers. By harnessing the power of IPF's scientific expertise, you can safeguard your nitrogen investments and reduce these costly losses. Enhanced Efficiency Fertilisers “EEFs” present an opportunity for farmers to embrace proven technology to maximise yield potential whilst helping reduce environmental impact. EEFs help limit nitrogen losses, assisting your crops to use nitrogen more efficiently. There is potential for EEFs to help reduce greenhouse gas emissions from agriculture, particularly nitrous oxide (N2O) and the indirect greenhouse gas ammonia (NH3).
Volatisation
It occurs when applied nitrogen, in the form of urea, converts into gaseous ammonia and escapes into the atmosphere. This process can lead to a loss of valuable nitrogen for crops.
Denitrification
It occurs when applied nitrogen, in the form of urea, converts into gaseous ammonia and escapes into the atmosphere. This process can lead to a loss of valuable nitrogen for crops.
Leaching
Leaching on farms refers to the downward movement of nutrients like nitrogen through the soil, potentially reaching groundwater or water bodies. This can result in nutrient loss and water pollution, affecting both crop productivity and environmental quality.
Enhanced Efficiency Fertilisers
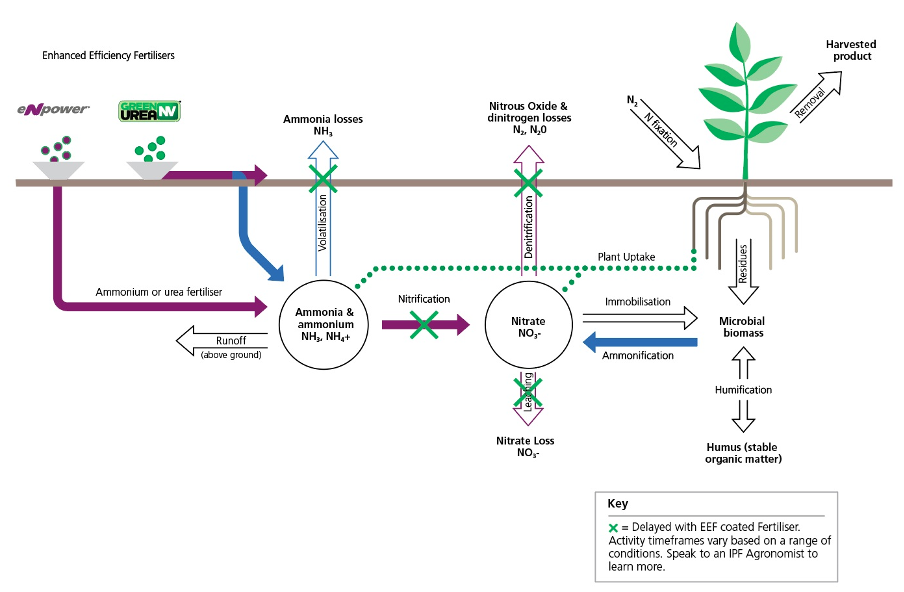
Surface applying urea? – Green Urea

Sub-surface applying nitrogen? - eNpower
By reducing nitrogen losses, eNpower® can provide a more sustained nitrogen supply to the crop in line with crop needs, resulting in yield and quality improvements through reducing denitrification & leaching.

